Arrest Of Cervical Dilation - Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm).
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm).
Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm).
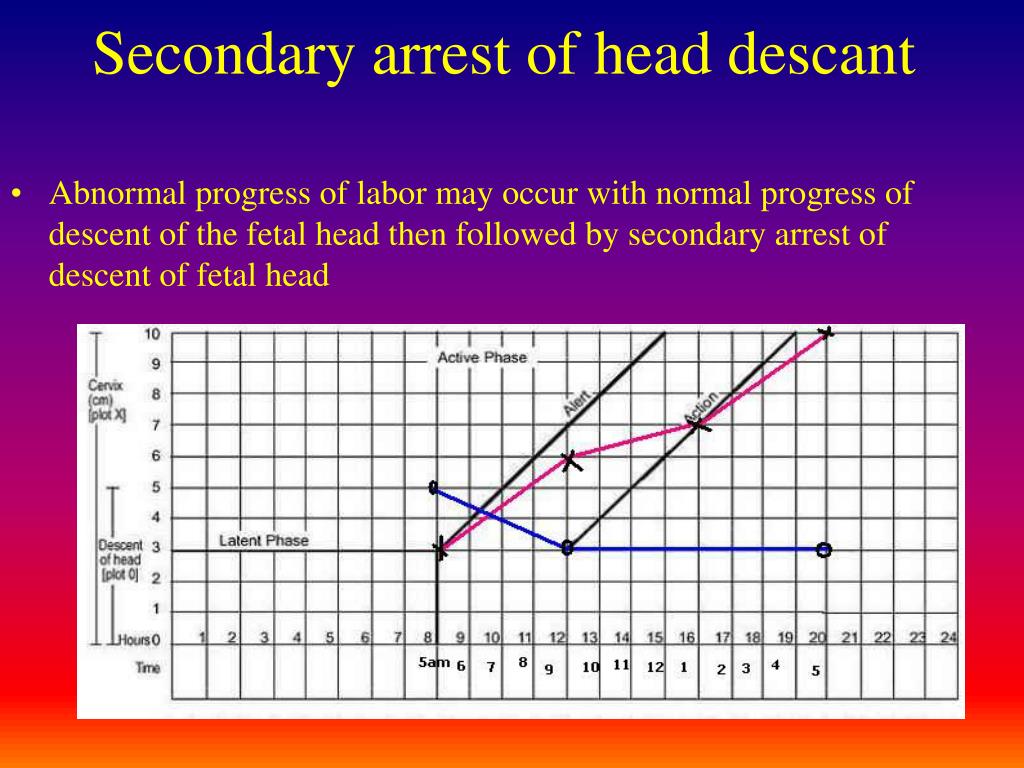
ABNORMAL LABOR NORMAL LABOR PROGRESSION STAGES AND PHASES
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
PPT Partograph PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4710660
Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm). Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and.
Cervical Dilation & Effacement Training Models Etsy
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm). Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for.
thunder bear and wren Midwife's Appointment Dilated and Effaced
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm). Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for.
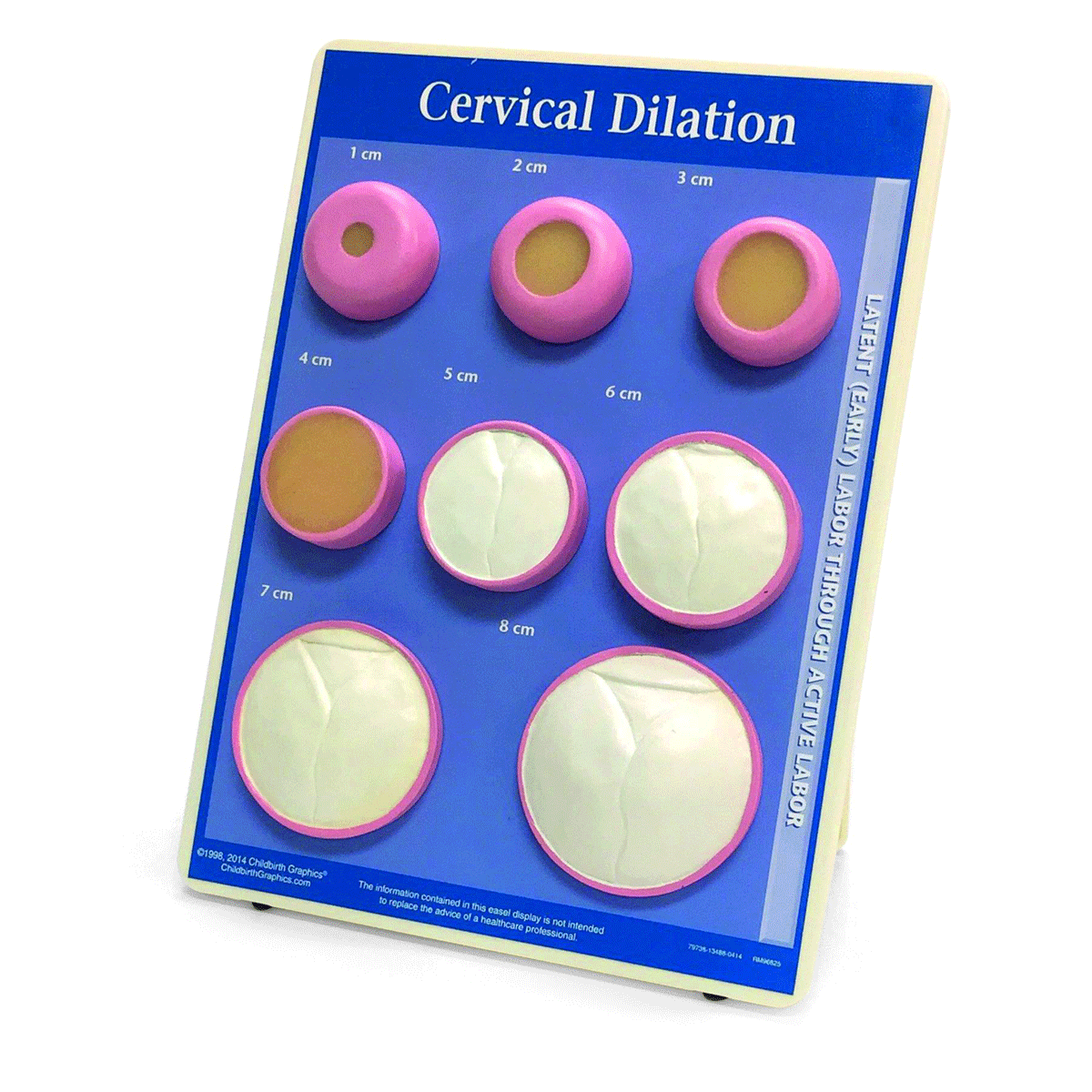
Cervical Effacement Dilation Model Childbirth Graphics
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
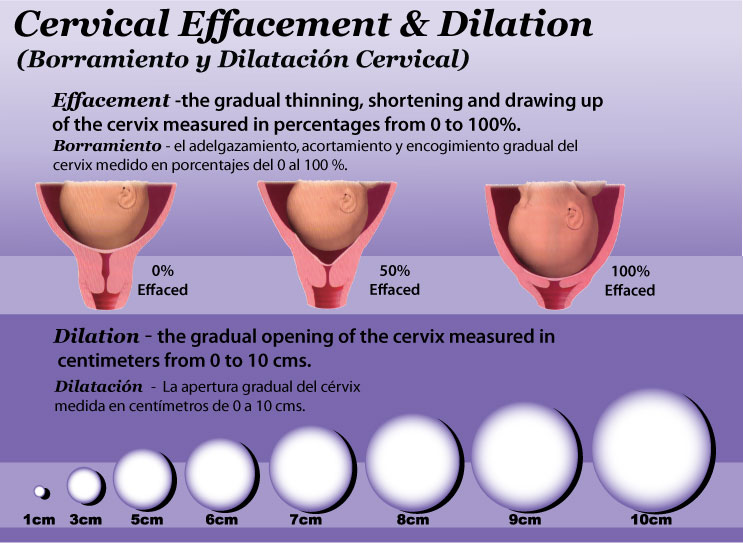
Cervical Effacement and Dilation Chart
Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
Cervical effacement and dilatation chart poster Zazzle
Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
Refining the clinical definition of active phase arrest of dilation in
Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
Dilation of the Cervix Play by Play — MMW Womens Health
Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated to 6 cm). Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for.
Dilation and Cervical Effacement chart Dilations, Cervical effacement
Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the. Web arrest of labor should not be diagnosed before active labor begins (i.e., the cervix is dilated.
Web Arrest Of Labor Should Not Be Diagnosed Before Active Labor Begins (I.e., The Cervix Is Dilated To 6 Cm).
Web during active labor (after 4 cm), the cervix should progressively dilate at a rate of no less than 1.2 cm/hour (for first babies) to. Web labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the.